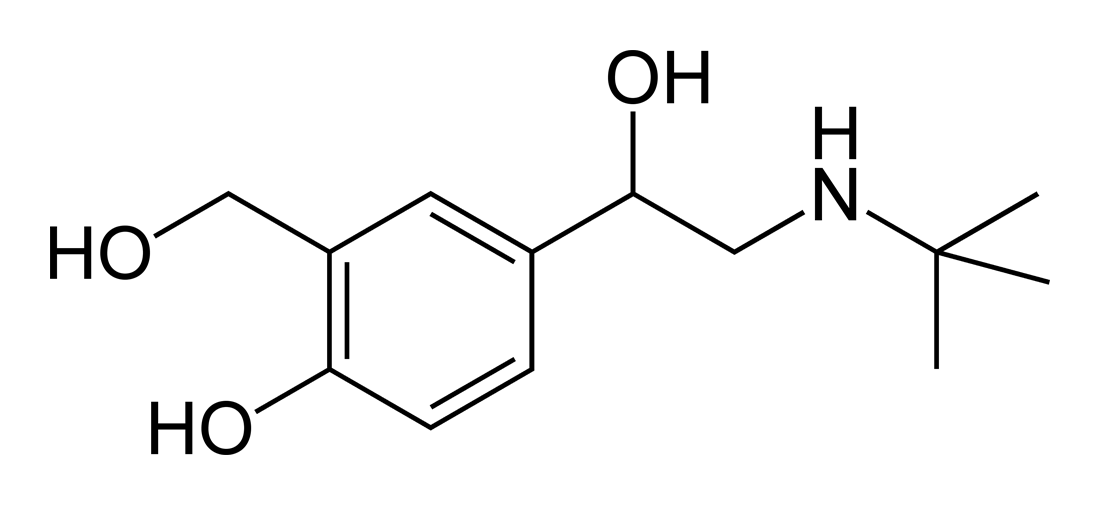
Salbutamol - for asthma
On WHO Model List of Essential Medicines : YES
Alternative names: salbutamol sulfate, Ventolin
Salbutamol or albuterol belongs to the family of medicines known as adrenergic bronchodilators and is marketed as Ventolin among other brand names. It is used to treat or prevent bronchospasm in patients with asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, and other lung diseases and relieve cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and troubled breathing by increasing the flow of air through the bronchial tubes.
 Salbutamol was the first selective β2-receptor agonist to be marketed in 1968 and has been used for the treatment of asthma ever since. It was approved for use in the US by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 1982.
Salbutamol was the first selective β2-receptor agonist to be marketed in 1968 and has been used for the treatment of asthma ever since. It was approved for use in the US by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 1982.
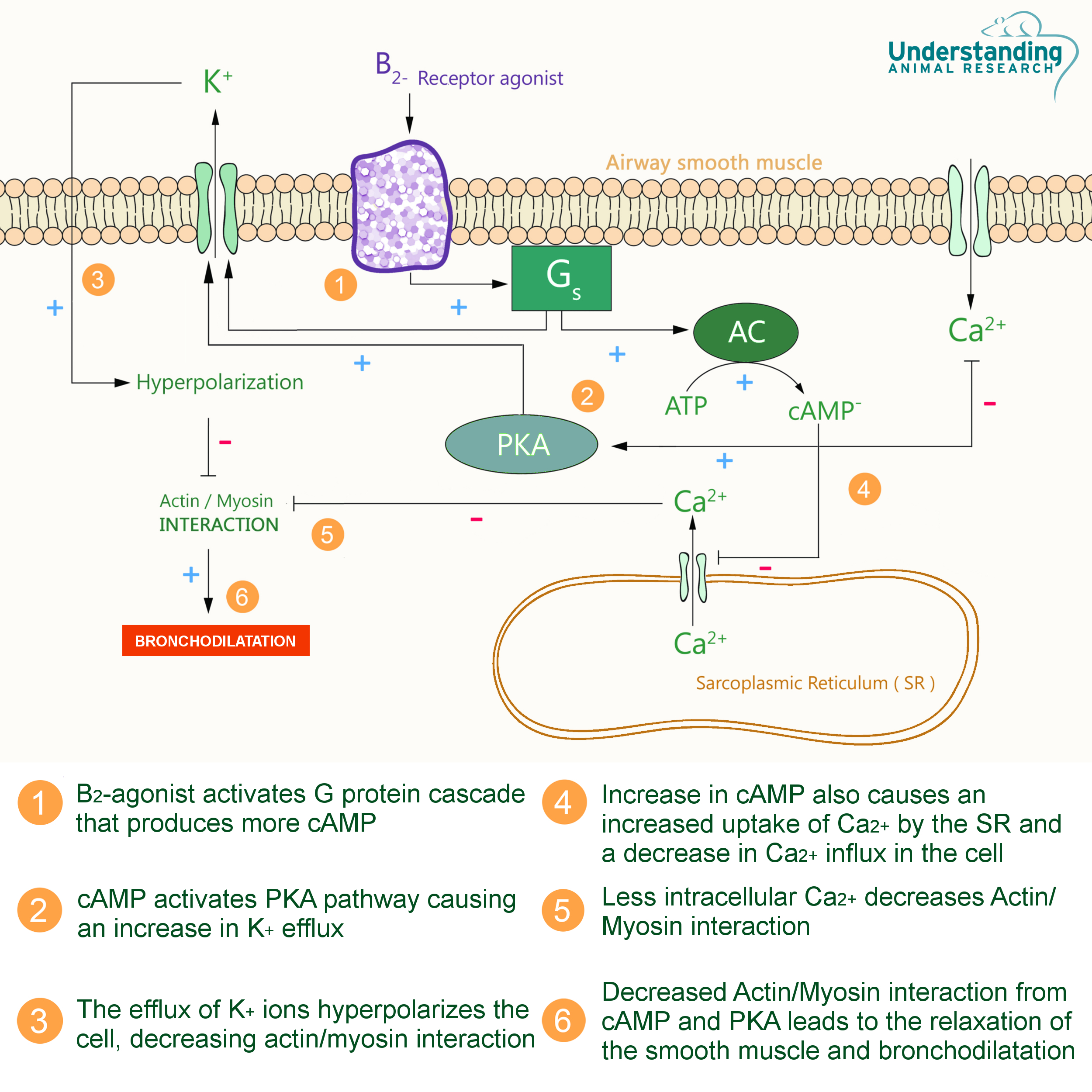
Salbutamol is inhaled to directly affect the bronchial smooth muscle within five to 20 minutes of dosing, though some relief is immediately seen. β2-receptor agonists cause the smooth muscles in the lungs to relax and the bronchial passages to dilate, the vasodilatation in muscles ant the liver, the uterine muscles to relax and insulin to be released. Beta-adrenergic receptors are coupled to an enzyme that produces a messenger (cAMP) that is responsible for decreasing calcium concentrations within the cells. β2 agonists also open large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels and thereby tend to hyperpolarize airway smooth muscle cells. The combination of the decreased intracellular calcium, increased membrane potassium conductance and decreased myosin light chain kinase activity leads to smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation.
Toxicology report
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8067892
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs002040050059
Last edited: 26 May 2016 11:17
