Amoxicillin - an antibiotic
On WHO Model List of Essential Medicines : YES
Alternative names: Amoxil, Polymox, Trimox, Wymox
Amoxicillin is a penicillin derived antibiotic used against bacteria. It is used to treat many different types of infections caused by bacteria, such as tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, gonorrhoea, and ear, nose, throat, skin or urinary infections.
Amoxicillin was discovered by scientists at Beecham Research Laboratories in 1972.
The narrow spectrum of antimicrobial activity of the penicillins, led to the search for derivatives of penicillin which could treat a wider range of infections. The first important step forward was the development of ampicillin. Ampicillin had a broader spectrum of activity than either of the original penicillins and allowed doctors to treat a broader range of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative infections.
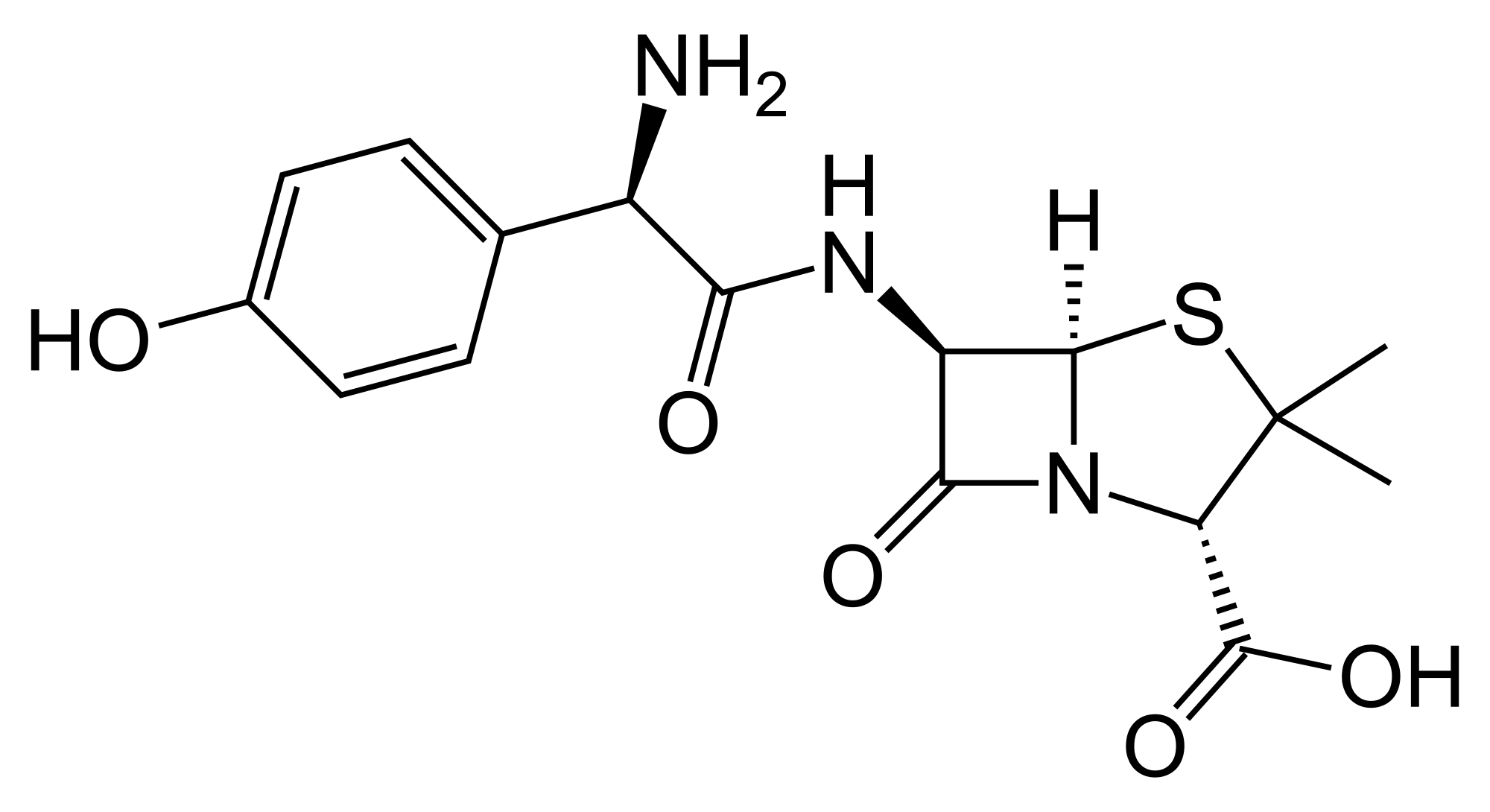
Further developments led to amoxicillin, with improved duration of action. It differs structurally from ampicillin merely by having an additional hydroxyl group on the benzene ring. The main difference between ampicillin and amoxicillin is that amoxicillin is slightly more lipid soluble. As a result, amoxicillin may kill bacteria slightly quicker.
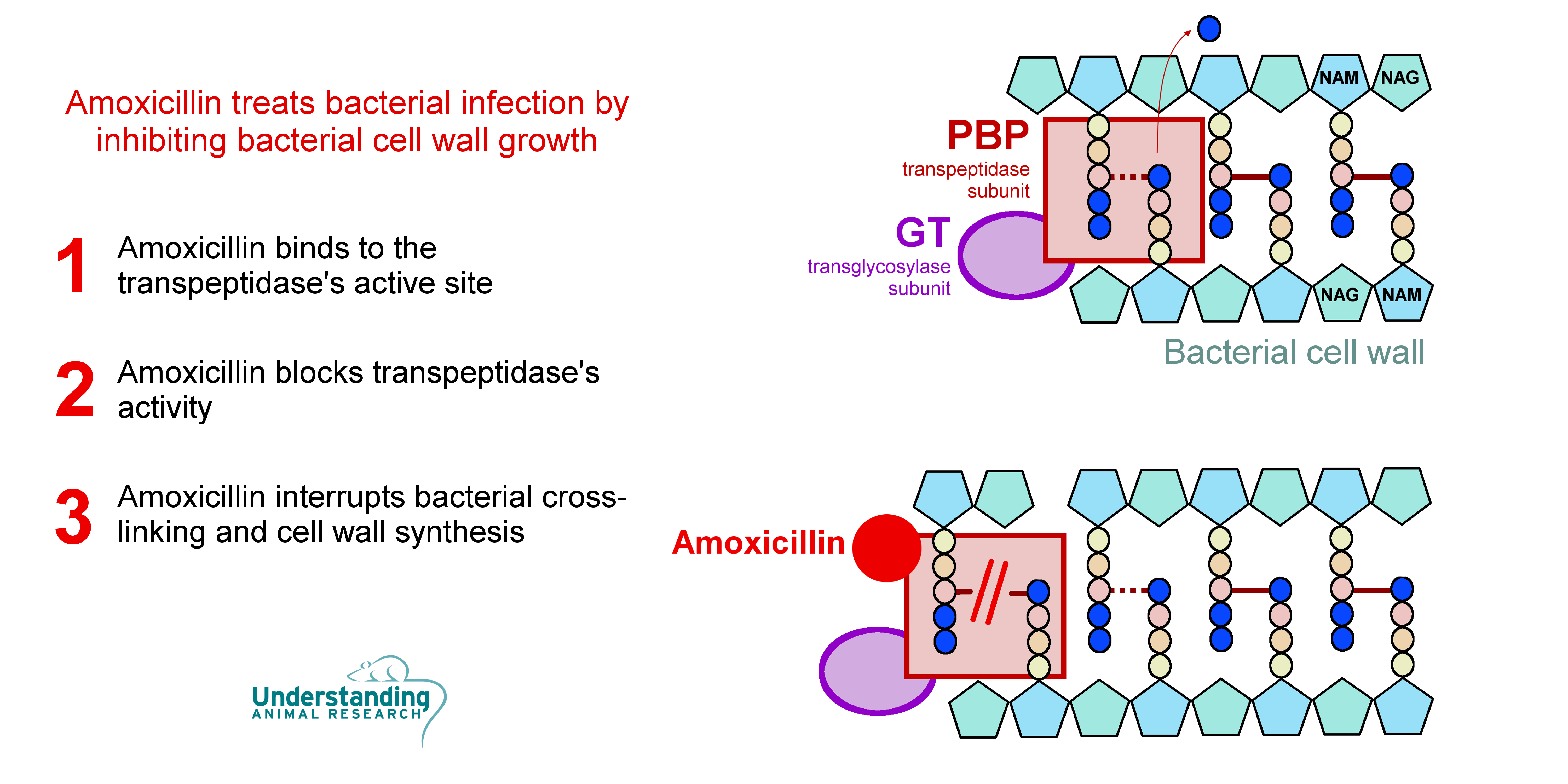
Amoxicillin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. It inhibits cross-linkage of a major component of the cell walls of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria – linear peptidoglycan polymer chains.
Amoxicillin first became available in 1972 and, today, there are many brands and forms of amoxicillin available.
Toxicology report:
http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2002/21-456_Aciphex_Pharmr.pdf
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/DevelopmentResources/ucm071718.pdf
http://www.drugs.com/pro/amoxicillin.html
Last edited: 4 August 2016 14:11
