Bisoprolol fumarate - beta-blocker hypertension treatment
On WHO Model List of Essential Medicines : YES
Alternative names: Concor
Bisoprolol fumarate is part of a group of drugs called beta-blockers. Beta-blockers affect the heart and blood circulation and are used to treat cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension. Beta blockers block the action of catecholamines - epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) - on adrenergic beta receptors of the sympathetic nervous system which mediates the fight-or-flight response.
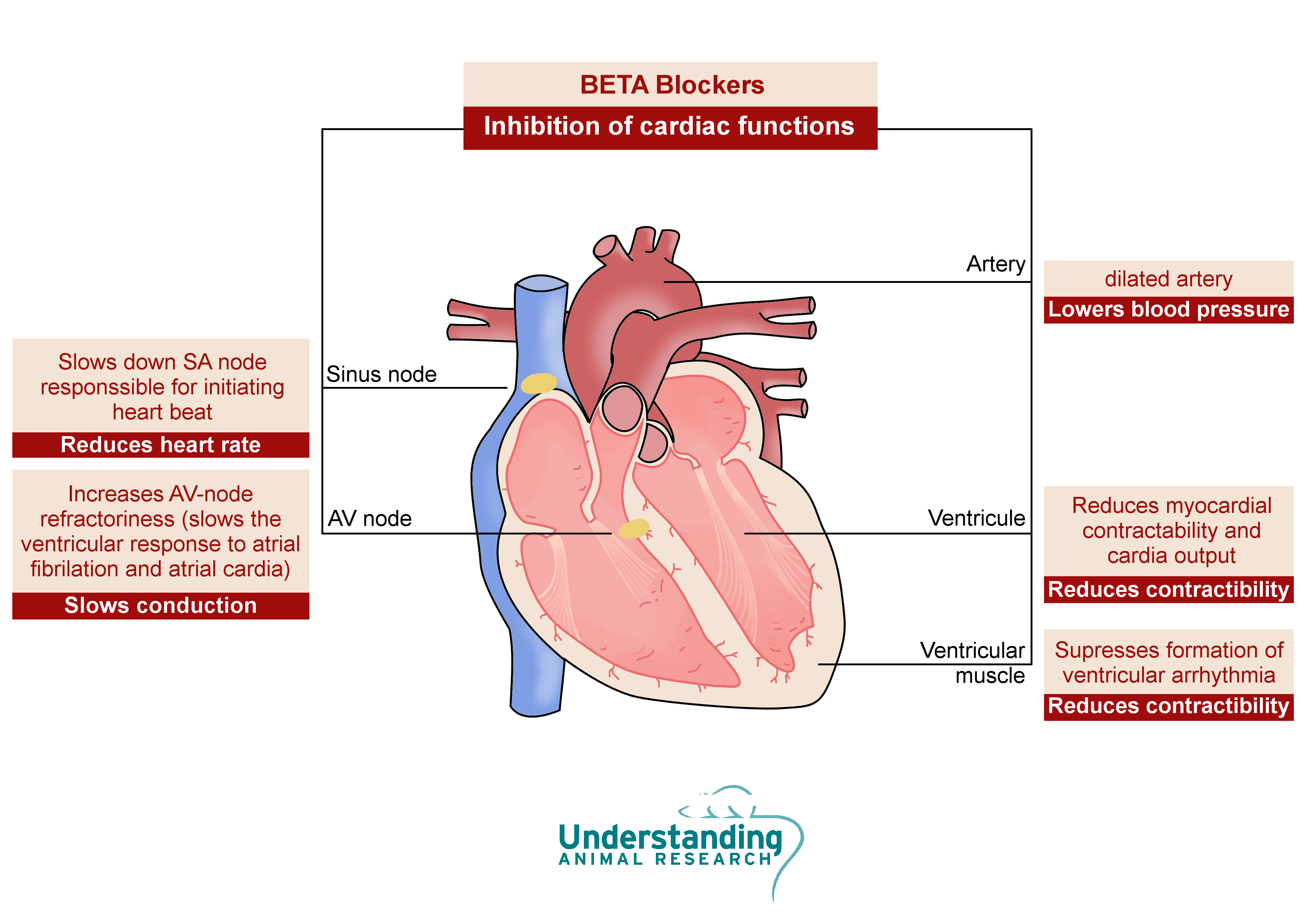
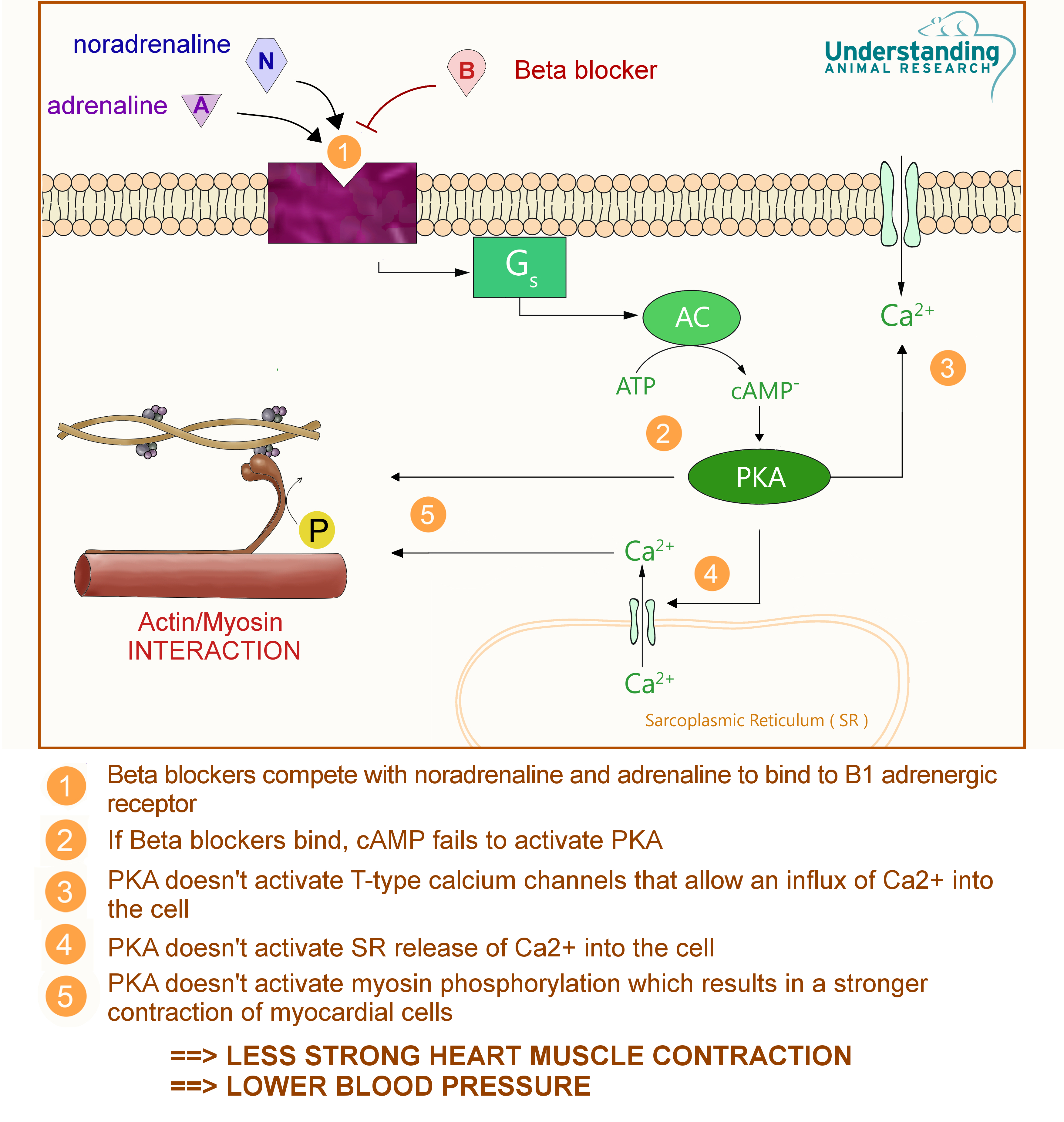
Bisoprolol fumarate is cardioprotective because it selectively and competitively blocks catecholamine - more currently known as adrenalin – stimulation of the β1 adrenergic receptors, which is mainly found in the heart muscle cells, heart conduction tissue and some kidney cells. Normally, stimulation of the β1 adrenoreceptor by adrenalin and noradrenalin activates a signalling cascade that ultimately leads to increased contractility of the heart muscle and increased heart rate of the heart pacemaker. Bisoprolol competitively blocks the activation of this cascade, so decreases the adrenergic tone/stimulation of the heart muscle and pacemaker cells. This leads to less contractility of the heart muscle and a lowered heart rate , which is ultimately benificial for hypertension because it reduces blood pressure.
The US Food and Drug administration (FDA) approved an application of Bisoprolol fumarate as a new molecular entity in July 1992.
Toxicology report
http://www.bisoprolol-slides.info/homesite/teaser.pdf
http://ogyei.gov.hu/kiseroirat/ph/ph_0000033377.pdf
Last edited: 4 August 2016 14:27
